Thermistors Tech Information
What is PTC thermistor? What differences between linear silicon PTC thermistor and ceramic switching PTC thermistors? What does the 3 Ceramic PTC thermistors characteristics Resistance vs. Temperature, Voltage vs, Current, Current vs. Time mean? Glossary Definition such as PTC Thermistor Zero Power Resistance, non-trip current, trip current, Curie temperature, reference temperature, etc.
Ceramic PTC thermistors manufacturing starts from mixtures of barium carbonate, titanium oxide and other materials whose composition produces the desired electrical and thermal characteristics are ground, mixed and compressed into disks or rectangle shape, then sintered at high temperatures Afterwards, they are carefully contacted, provided with connection elements depending on the version and finally coated or encased.
What is the appropriate PTC Thermistors storage and Environmental conditions? What should be taken care in PTC Thermistors handling, mounting? When soldering, care must be taken that the thermistor are not damaged by excessive heat. The maximum temperature, maximum time spans and minimum distances should be observed. PTC Thermistors Sealing Potting and Cleaning rules should be observed.
In selecting PTC Thermistors for Over Current overload Protection, the following items should be taken into consideration, Voltage, Current, PTC Thermistors application environment .
PTC thermistors RT Characteristics linear silicon vs switching ceramic
What is difference of PTC Thermistor Temperature Sensor between Linear Silicon and Switching Ceramic?What is specific Silicon PTC Silistor and Cermic CPTC Advantage? How to choose? How to find corresponding AMWEI part to cross NXP KTY81 83 84, Epcos B59051D11**A040 series, Murata PTFM PTFL Series POSISTOR cross?
To protect telecom installations against the effects of lightning, induced energies or the harmful direct contact between telecom and mains lines, protection components are used either directly on the line card or in the main distribution frame. Here Ceramic PTC Thermistors have clear advantages in comparison to Polymer PTC Thermistors. Considerations and selection criteria are presented in the following article.
Test and measuring instruments, such as oscilloscopes and digital multimeters, can be easily damaged if excessive voltages are applied across their input terminals.
Simple and effective overload protection can be provided by connecting a high-voltage PTC Thermistors in series with the instrument.
PTC Thermistor is useful to monitor the FET’s temperature. When the FET’s temperature approaches the maximum rating, PTC Thermistor turns the transistor on. In this way the FET’s gate voltage decreases below its threshold level and the FET is turned off. When the FET’s temperature returns within the rating, normal operation returns. There is therefore no need to exchange protecting elements like fuses.
PTC Thermistor limit temperature sensors offer perfect protection against overheating and thermal damage. A PTC Thermistor makes it possible to intervene in operation of the power stage directly and with a measured response in the event of excess temperature. At room temperature, the PTC Thermistor has a relatively low resistance. As the temperature rises, this initially drops slightly and then rises steeply. This steep section of the R/T characteristic is used for temperature measurement.
Thermal management is becoming increasingly important as a result of miniaturization, rising power consumption and tougher requirements on reliability. At the same time the number of hot spots on boards and equipment is also growing. The steep and rapid change in resistance of PTC thermistor sensors with temperature allows several hot spots to be monitored with a simple circuit.
What is NTC Thermistor? As defined by IEC 60539, NTC thermistor are thermally sensitive semiconductor resistors which show a decrease in resistance as temperature increases. Sensitivity to temperature, electrical power input, changes in thermal conductivity. Find How the NTC Thermistor Glossary R25 Beta, Thermal Time Constant, etc is defined.
β Beta value is an indication of the shape of the curve that represents the relationship between the resistance and the temperature of a particular Thermistor. Calculate the beta value to achieve the right characteristic at a given temperature vs the resistance for a specific application. it is a vital step in the component selection process. Read More >>
NTC thermistor starting materials are different oxides of metals such as manganese, iron, cobalt, nickel, copper and zinc. The oxides are milled to a powdery mass, mixed with a plastic binder and then compressed into the desired shape. The blanks are then sintered at high temperatures to produce the polycrystalline thermistor body. Disks are contacted by baking a silver paste onto the flat surfaces, fitted with leads or tab connectors, coated or additionally incorporated in different kinds of housing.
Read More >>
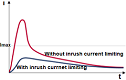
There are 3 major criteria for selecting the best NTC Thermistor inrush current limiter, surge suppressor for an application:
1) Rated resistance (R25), 2) Maximum permissible continuous current under rated operating conditions (Imax, DC or RMS values for AC), 3) Maximum capacitance CT to be switched
Read More >>
The high sensitivity of an NTC thermistor makes it an ideal candidate for temperature sensing applications. These low-cost NTC thermistor sensors are normally used for a temperature range of -40C to +300C.
Selection criteria are: Temperature range -Resistance range -Measuring accuracy-Environment (surrounding medium)-Response time-Dimensional requirements.
Application precaution, application in Wheatstone bridge, Thermostat Circuit, charging control unit for Battery Pack, Refrigerator can be founded.
Read More >>
Characteristically, NiCd or NiMH secondary batteries cannot be charged over a specified temperature, and they can be quickly charged only within a specified temperature range. NTC Thermistor is used to promptly detect the temperature range that will allow quick charging. Detects temperature rises of the battery cell during charging. Detects the ambient temperature that will allow quick charging. Detects heat generation of a battery cell caused by abnormal current. Performs temperature compensation for voltage measurement for display of the remaining amount of energy.
Read More>>
A wide range of AMWEI NTC and PTC Thermistors is available to protect the inputs of power supplies from excessive inrush and surge currents. These components are characterized by their high reliability and the fact that they require only minimal additional design-in effort.
Read More >>
Linear Silicon PTC Thermistor Temperature Sensor
PTC Thermistor Current Protect Resettable Fuse
PTC Thermistor for High Voltage Current Surge Telecom Protect
PTC Thermistor Limit Temperature Sensor
PTC Thermistor Heater
Lighting Switching Time Delay
PTC Motor Sensor, 1 PTC Single Sensor & 3 PTCs triple Sensor
PTC Thermistor Motor Starter
Inrush Current Limiter Power NTC Thermistor, Surge Suppression
Radial Leaded Resin Coated NTC Thermistor Temperature Sensor
Axial Leaded Glass Encapsulated NTC Thermistor Temperature Sensor
Radial Leaded Glass Encapsulated NTC Thermistor Temperature Sensor
NTC Thermistor Temperature Sensor Probe Assembly
Radial Lead Resin Coated NTC Thermistor for Temperature Measurement Compensation
NTC Thermistor SMD Part, 0805 0603 0402